Control of Cart Pole with State-Action Value Functions
Published:
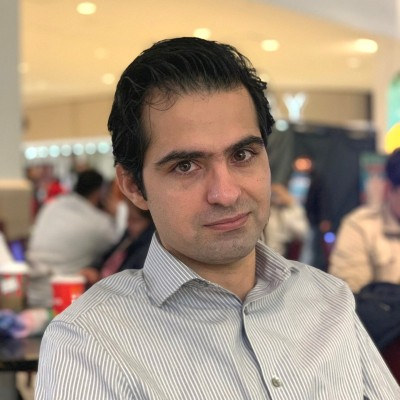
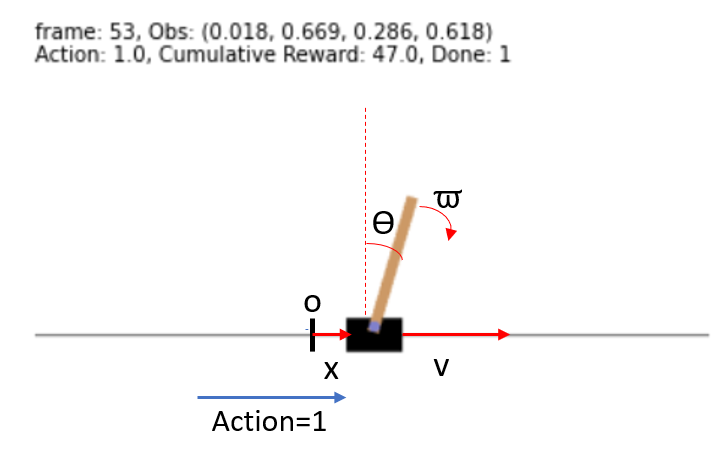
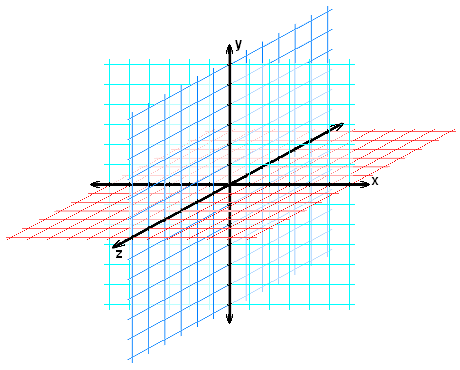
The general form of the cart-pole is shown in the following figure. Note that we have a four dimension state representation $[x, v, \theta, \omega]^T$. You can see the idea of quantization of continuous feature space to discrete state space in the following figure (shown for 3D, but the idea is the same).
State-Action Value Functions
The idea of state-action value functions (Q-values) is shown in the following figure. The idea is simple. For each situation (state) and all available moves (actions) we calculate the cumulative reward for that state-action pair. We start from random initializations for these Q-values, and keep updating them till we converge (or we are at the end of the number of iterations!).
$\epsilon$—Greedy Policy
The state-action value functions (Q-values) tell us what return different actions at different states can give us. Now we need to define how to pick actions. Now we can be deterministic or stochastic, but for simplicity we focus on the deterministic approach.
An intuitive policy would be: At each state $s$, pick the action $a$ that gives us the highest (estimated) reward. This is a greedy policy, and this idea is also called exploitaion. The problem with this approch is that the rewards, which are recorder in a table in terms of the Q-values, are estimated, hence they are not reliable. We need to explore other options to improve our estimates of the Q-values. This idea is called exploration. To balance this, we usually use an algorithm, called $\epsilon-$greedy. This algorithm is summarized in the following.

Now, we should note that as we move forward in the simulations, we decrease decrease $\epsilon$ becasue we do not need exploration that much. Also, it is safe to assume that as we move forward in the simulations the benefits of the explorations in finding the optimal policy decreases. Hence we use a decreasing epsilon.
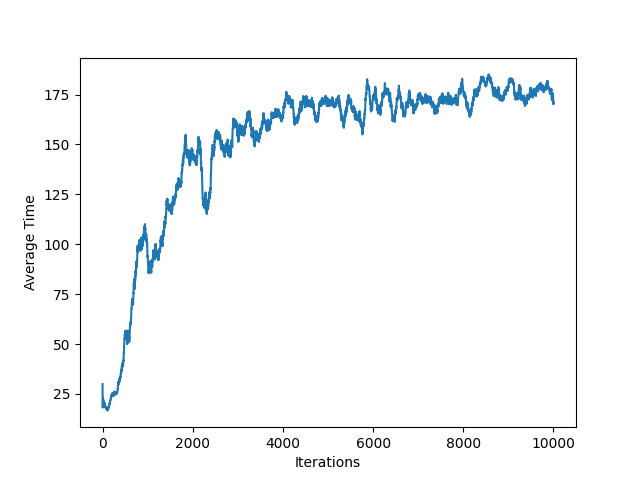
The moving average of the average survival time of the policy is shown in the following figure:
To see the Github repository for this project, see Github.
